CHAPTER 9
Misconceptions & Myths On Search Engine Marketing
Misunderstanding & Myths | Search Engine Marketing
The previous years have witnessed very many misunderstandings about the way search engines work. A first-timer SEO would find it difficult to identify the essentials for the operation of search engines. Here, in this chapter, we will identify the myths and explain the reality.
Search Engine Submission
In the late 1990s, otherwise known as the classical SEO times, search engines made use of submission forms that were included in the process of optimization. Keyword information would be used to tag sites and pages before the site owners made submissions to search engines. Once the submission is done, a bot is expected to crawl and all resources would soon be added to their index. That was SEO.
It did not take too long before this process was replaced with crawl-based engines because the it didn’t scale as expected. Search engine submission eventually became unnecessary and out of use since 2001. Various engines explain that the submitted URLs are not used, websites should work on earning links from other pages. This is expected to expose your content to the engines naturally.
It is not impossible to locate some submission pages (there’s an example for Bing). However these are remnants from the past, they remain unimportant in the present day practice of SEO. If by chance, a SEO still using search engine submission approaches you, be wary enough to ignore such and look for a functioning SEO. Let’s assume that they did use the submission to crawl your site, your chances of getting enough links and increasing your rank in search queries are lean.

Meta Tags
There was such a time that meta tags were crucial parts of the process of SEO. You were only required to add the keywords you would prefer your site to be ranked for, your page is then provided for queries that included such words. It didn’t take long for this procedure to be jettisoned as an essential ranking sign by the main search engines.
Other forms of tags, especially the title tag and meta description tag(covered previously in this guide), are important for quality SEO. Also, a consequential tool for regulating the access of crawlers is the meta robots tag. It is still quite necessary to comprehend the usefulness of meta tags, but it should be noted that SEO does not focus on them.
Keyword Stuffing
Have you come across a page that appears spammy before? You’d see something like this:
“Bob’s cheap Seattle plumber is the best cheap Seattle plumber for all your plumbing needs. Contact a cheap Seattle plumber before it’s too late.”
Another myth very common in SEO concerns keyword density —the number of words on a page divided by the number of instances of a given keyword. It is believed that keyword density is employed by search engines for calculating ranks and applicability.
Even though the myth has been proven to be untrue, it still continues to spread. A lot of SEO tools continue to operate with the consciousness that keyword density is a consequential measure. It should be noted that it isn’t. Keywords should rather be used appropriately. Earning links still remains more important to a webpage than the keyword density.
Paid Search Helps Bolster Organic Results
Another widely accepted myth is that the more you spend on search engine marketing, otherwise known as pay per click, your SEO rankings receive the boost.
Using our experience and studies, there has been no proof that sponsored adverts improves search results. The major search engines, Google, Bing, Yahoo! all have walls made to stop this kind of change.
Citing Google as an example, clients who spent a lot of money on advertising per month affirm that the relationship notwithstanding, they still cannot acquire unique treatment from the search quality and web spam teams. Since search engines continue to operate this way, the opinion about sponsored search engine marketing in improving search results is a myth.
SEARCH ENGINE SPAM
In the instance of a search, spam is inevitable. The act of spamming engines- making pages that are supposed to increase rankings- continues to grow since the mid-1990s.
The implication is serious. It was reported that a certain SEO that ranking high in Google’s search results for the ‘buy Viagra’ query had the potential of earning up to $20,000 in revenue. It, therefore no longer comes as a surprise that maneuvering the engines remain a famous practice. All the same, the act has become a whole lot more tedious and less encouraging for two different reasons:
1. Not Worth the Effort
Generally, spam is not appreciated by users and the search engines oppose it for financial reasons. A lot of people accept that the edge Google has over other search engines is the check it has over spam as well as the capacity to eliminate it. It is without doubt that other search engines expend their resources on this. Although, spam could work sometimes, the amount of energy it takes for it to work out and the fact that it almost has no long-term reward make the effort quite worthless.
So, in exchange for an eventual waste of efforts, a value-added long term strategy proves to be a lot better.
2. Smarter Engines
Search engines have taken the time and effort it requires to rise to the occasion. They have worked on the development of exceptional strategies for stopping spam exploitation. Also, creating great difficulties for attempts at influencing intended algorithms. Measures such as historical data and statistical analysis has drastically reduced the essence of search spam, rewarding rule-abiding SEOs.
Lately, Google’s Panda update brought in smarter machines learning algorithms to fight spam and pages that are of inconsequential worth. Search engine marketing is relentless in its efforts to create ways of producing accurate results.
It is without debate that we do not encourage using spam strategies. However, in assisting the SEOs that need aid when their websites are penalized, we admit that it is a worthy venture, to explain a few of the criteria search engines utilize in recognizing spam. If you need more information about spam, you should view Google’s Webmaster Guidelinesand Bing’s Webmaster FAQs (PDF).
However, this should be noted: making use of manipulative methods are in no way helpful. Most often than not, search engines place heavy punishments on such sites.
PAGE-LEVEL SPAM ANALYSIS
Search engines carry out spam analysis through individual pages and entire websites (domains). We’ll examine first the way search engines estimate manipulative acts on the URL level.
Keyword Stuffing
Keyword stuffing remains one of the most conspicuous methods of spamming. This is the practice of scattering the keyword terms or phrases on a page, using the keyword phrase or term more times than necessary with the aim of achieving relevance to queries on search engines. It has been discussed earlier that this method is highly worthless.
Examining a page to discover stuffed keywords has proven not to be very difficult. What’s more, search engines’ algorithm can easily carry out the task. To get more information about this act, you can read a blog post from the head of Google’s web spam team: SEO Tip: Avoid Keyword Stuffing

Manipulative Linking
Manipulative link acquisition as one of the most widely known methods of web spam tries to juice the fact that search engines make use of link popularity to dubiously boost their visibility. The search engines find this form of spamming very difficult to control, owing to the fact that it could occur in various ways. Some of the ways this could occur are:
● Reciprocal link exchange programs: This involves creating pages that link to one another to improve link popularity. Search engines can identify and depreciate them quite easily because they are used in a specific pattern.
● Link schemes: These are “link farms” and “link networks” where false sites are developed and used only as sources of link to improve link fame. Search engines control these sites by discovering ties between link overlap, site registrations and such other means.
● Paid links: Many sites in dire need of higher rankings get involved in the purchase of links in exchange for money. This could lead to a large circle of sales and purchase of links. Search engines have made efforts to stop them (especially Google). However, this method continues to offer value to the sites involved.
● Low quality directory links: These links often come in handy in the process of manipulation. Many web directories that allow payment for link placement are in existence, having the reputation of legitimate websites. Google controls this sort of sites by eliminating the PageRank score from the toolbar, or decreasing it. This does not occur in every case.
The search engines have identified more manipulative link developing methods. Most often than not, they have discovered algorithm strategies for controlling them. New spam systems continue to surface and engineers persist in their fight against them by employing human reviews, algorithms and the receipt of the reports of spamming from webmasters and SEOs.
Cloaking
It is an acceptable practice to search engines that engine’s crawlers and humans have access to the same content. In addition to other implications, this implies that text should not be hidden in the HTML code in a website that users (the regular visitor) can not view.
In the instance that the rule is not followed, it is referred to as ‘cloaking’. Thus, search engines see to it that such pages do not receive high ranking in their results. Cloaking is possible in various forms and for many reasons, either positive or negative. Some cloaking acts aid user experience. Therefore, search engines do not penalize such sites. To understand cloaking better, as well as the dangers in using different approaches, view on White Hat Cloaking.
Low Value Pages
Low value pages are not particularly web spam but search engines all have ways of identifying pages that offer valuable content to its users. The most usually scanned kind of pages are duplicate content, contents with thin web popularity and content pages that are dynamically generated and offer minute value. Engines do not usually add these pages. Hence, they screen them out with different link and content analysis algorithms.
In 2011, Google’s Panda update made serious efforts to decrease contents with low quality all through the web, and Google continues to iterate on this process.
DOMAIN LEVEL SPAM ANALYSIS
Apart from examining different pages for spam, it is also possible for search engines to recognize properties all through subdomains and domains that could penalize them as spam.
Linking Practices
As it is the case with individual pages, search engines can also scan the types of links and referrals sent to a site. Such websites that are involved in manipulative practices will either be banned from the index or their traffic will reduce. Some examples are in previous posts, including Widgetbait Gone Wild and the more current coverage of the JC Penney Google penalty.
Trustworthiness
Some websites have trusted status because they earned it. Such websites are usually handled in a different way, compared to those that do not have such status. SEOs have confirmed the double standards that are used in examining independent websites, big brands and sites that are of high significance in comparison to other sites that are new and not independent. Trust, for search engines is determined by the links earned by your domain. For instance, if a website creates low quality contents and then purchases links from spammy directories, such a website will most likely be faced with ranking problems. Conversely, if the same content is posted on Wikipedia, with all the spammy links, there would be no ranking problems. This preferential treatment comes as a result of trust and authority.
Inbound links can also help to build such trust. If it happens that a website has earned a lot of links from editorial sources that are of high quality such as CNN.com or Cornell.edu, a number of suspicious links or copied content would not matter.
Content Value
As explained above, a page’s value is evaluated partly on the basis of the user’s experience and the originality. This also applies to the whole domain. Websites that offer low value, non-value contents or lack uniqueness are possibly unable to rank, regardless of the optimization of the on- and off- page SEO. It is undesirable to search engines that a lot of copies of Wikipedia fills up their indexes. Therefore, they utilize algorithmic and other manual strategies to control it.
Search engine marketing examines how effective their SEO results are on a regular basis. They have metrics for the number of times users click on a particular result or exit a page promptly in search of other results. This implies that the result offered did not meet the user’s need.
Therefore, ranking for query is not sufficient. An earned ranking should be proved consistently.
So How Do You Know If You’ve Been Bad?
Identifying flagging might be difficult. Search engines’ algorithm could change, and it could happen that something was changed on your website that affected your rankings negatively. Therefore, assumptions about penalties should not be made. You should check the following first:
 If the list below does not apply, check the flowchart underneath for more particular guidance.
If the list below does not apply, check the flowchart underneath for more particular guidance.
Errors
Check errors on your website that could have restrained crawling. Google’s Search Console will serve you well in this endeavor and for free.
Changes
It is possible that you may have effected changes to your website or individual pages that may have affected the way search engines see your content. (on-page changes, internal link structure changes, content moves, etc.).
Similarity
You could also examine other websites that use identical backlink profiles as yours, whether or not they have lost their ranking too. It is a possibility for search engines to update their ranking algorithms. When this happens, the value of links can shift. This will lead to the movement of rank.
Duplicate Content
Many modern websites are swarmed with issues of duplicate content, particularly when scale to enormous size. See the post on duplicate content to identify frequent issues.

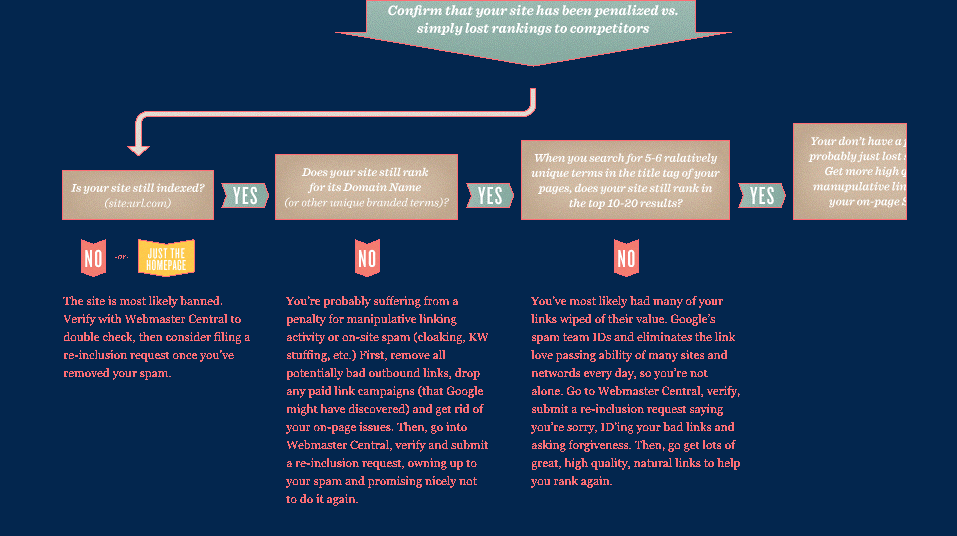
It is possible that this chart’s process will not be effective for all situations, the logic has been useful in recognizing spam flagging as well as mistaken flagging by the search engines, distinguishing them from fundamental drops in ranking. This page from Google (and the included YouTube video) could prove useful on this topic.
Getting Penalties Lifted
Attempts to request reconsideration or re-inclusion in search engines is usually both aching and abortive. Explanations on what happened and why are most often not given. Notwithstanding, it is necessary to have the knowledge of the proper steps to take when penalties are given.
- If your site is not registered with the engine’s Webmaster Tools service (Google’s and Bing’s), make sure it is. The registration increases the level of trust and ties between search engine teams and your website.
- Scrutinize the data in your Webmaster Tools accounts thoroughly, including crawl errors, broken pages, and spam alert messages. Sometimes, a mistaken spam flagging could be connected to issues of accessibility.
- Your reconsideration/re-inclusion request should be sent through the engine’s Webmaster Tools service, do not use the public form; this also increases the level of trust as well as the chance of receiving a feedback.
- Full disclosure is important if you would be considered. In the case of spamming, be open about all the activities you’ve been involved in such as the links you got through this method, how you acquired them and those who purchased from you. Search engines, especially Google usually use these details in enhancing their algorithms. When you keep information away from them, they would regard you are as deceptive and unyielding. This would reduce your chances of receiving feedback from them.
- Correct everything possible. Try to remove every bad link you’ve gathered, if any manipulation has occurred on your website (such as mentioned above), get rid of them before you tender your request.
- Be determined to wait. It could take a long while before you get a feedback. Also, re-inclusion is usually a long process. The request backlog is often enormous as hundreds and thousands of websites receive penalties weekly.
- In the event that you have a valuable brand on the web, re-inclusion can be hastened by approaching a personnel at an event or a conference. Search engineers usually get involved in search industry conferences (SMX, SES, Pubcon, etc.). The value of quickly being re-included can be the same as the price of admission.
It should be noted that it is not obligatory for search engines to remove penalties. They are backed by the law to refuse or accept any website or page. Therefore, inclusion should not be seen as a right, it is a privilege. Be careful and avoid the use of search engine marketing that you are not comfortable with. Otherwise, you could discover yourself in a fix.








